Apple Intelligence features may be landing on your iPhone, but that doesn’t mean they’ll stay fixed in place once they get there. Because they’re powered by artificial intelligence, Apple Intelligence capabilities have the potential to get smarter as Apple refines its models. And there’s always the possibility of Apple expanding what already-launched features can do.
The latter happened to Writing Tools with the iOS 18.2 update. Writing Tools arrived among the first batch of Apple Intelligence features in October’s iOS 18.1 release with the promise of improving your writing. Besides checking spelling and grammar, Writing Tools could also make suggestions on tone with presets that allow you to make any text you’ve written more professional, friendly or concise. There’s also a Rewrite option in Writing Tools for making wholesale changes to your document.
In my updated iOS 18 review, I wasn’t terribly complimentary toward Writing Tools. Aside from the Professional preset, which does a good job of observing the formal rules and structure that are a part of formal writing, the other options seemed to be satisfied with swapping in a few synonyms and sanding off any hint of writing voice. The end result usually resulted in robotic text — quite the opposite of what I think we should strive for in writing.
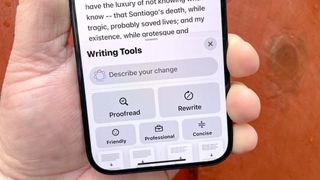
iOS 18.2 expands the arsenal of commands at Writing Tools’ disposal with a new Describe Your Change feature. Instead of relying on the presets, you can type out a text command like “make this more academic” or “make this sound more fun.” The idea seems to be to give you more control over the changes the AI makes to your writing.
Does the addition of Describe Your Change make me reassess the value of Writing Tools? And just how well does Apple Intelligence respond to your editing suggestions? I Took Describe Your Change for a test drive, and here’s what I found out.
How to use Describe Your Change in Writing Tools
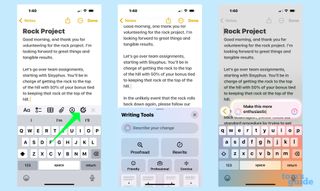
Describe Your Change works like any other part of Writing Tools, which is available to any iOS app that accepts text input. Just select the text you’re looking to improve and Writing Tools will appear in the pop-up menu that also contains commands like Copy, Paste and whatnot. Some built-in apps like Notes will also feature an Apple Intelligence icon in their toolbar that summons Writing Tools.
Describe Your Change is now listed at the top of the Writing Tools menu that slides up from the bottom of the screen. It’s a text field that appears above the Proofread and Rewrite buttons. Just tap on the field and type in directions for Writing Tools. Tap the up arrow in the right side of the text field to put Writing Tools to rework at recasting your text.
How Describe Your Change performs
To see how well Describe Your Change follows instructions, I tried three different passages that I wrote in Notes. Two of the test documents were originals; the third was a well-known bit of dialogue from a movie. In addition to seeing if Describe Your Change delivered the changes I was looking for, I also checked to see if the AI tool improved my writing.
Test 1: Make this more enthusiastic
In my first sample text, I wrote a memo to members of my team that describes our next project — rolling a rock endlessly up a hill. Let me tell you, Sisyphus is getting the short end of the stick with this assignment, so I wanted to see if the Describe Your Change command could make my instructions a little livelier.
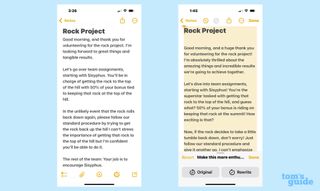
While Writing Tools has apparently decided that exclamation marks indicate enthusiasm, I do have to admit that AI did a credible job of making the prospect of rolling a rock up a hill sound very exciting. A passage in the original text where I said I was “looking forward to great things and tangible results” became a section where I talked up “the amazing things and incredible results we’re going to achieve together.”
Writing Tools can lay it on a little thick, inserting a “How exciting is that?” right after I explained to Sisyphus that 50% of his bonus was tied to keeping the rock at the top of the hill. That interjection came across as not terribly sincere. But overall, you can’t fault Writing Tools for making my original text more enthusiastic. Sisyphus is now addressed as “the superstar tasked with getting that rock to the top of the hill,” and the memo now ends with a “Good luck, and let’s rock this project!” I like to think the pun was intentional.
Test 2: Make this more humble and earnest
I wanted to see how Writing Tools responded to a request with multiple instructions, so I took a letter to Santa Claus that I would best describe as “brusque” and “demanding” to see if the AI could make it sound a little more accommodating. I asked Writing Tools to pump up the humility and make the requests for presents seem a little less like expectations.
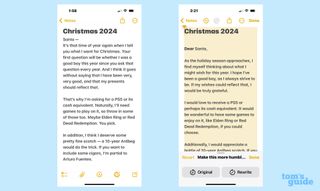
For the most part, Writing Tools did a decent job making me sound less like an expectant brat. A passage where I asked for a PS5 or its cash equivalent went largely unchecked, but my assumption that Santa would obviously bring games to go with my PS5 had the rough edges sanded off. (“It would be wonderful to have some games to enjoy on it,” the AI-assisted me told Santa.)
The strongest element with Writing Tools’ pass through my letter was that it really emphasized my gratitude for any gift Santa brought. An assertion that I had been a very good boy who deserved presents became something less assuming: “I hope I’ve been a good boy, as I always strive to be. If my wishes could reflect that, I would be truly grateful.” The first part of that last sentence is phrased a little awkwardly, but at least Writing Tools captured the sentiment I had suggested.
Test 3: Make this friendlier
So far we’ve seen what Writing Tools and Describe Your Change can do with my writing. But what about Academy Award-winning screenwriter Aaron Sorkin? If you’ve seen the film adaptation of his “A Few Good Men” play, you doubtlessly remember the “You can’t handle the truth” speech that Jack Nicholson gives in the climactic courtroom scene. And if you’re like me, you probably wondered, “What if that Marine colonel had just been a little nicer?”
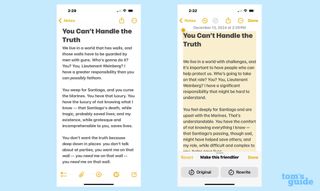
So I took that speech, pasted it into Notes and told the Describe Your Change tool to “Make this friendlier” — a pretty tall task given the ferocity of Colonel Jessep’s words. And Writing Tools may have sensed it wasn’t up to the task, as I got a message warning me that the feature really wasn’t designed for this kind of writing. Nevertheless, I opted to continue, just for the purpose of testing the limits of Describe Your Change.
To give Writing Tools credit, it did make the passage friendly, but that involved some serious rewriting to the point where the original intent of the speech was lost to the four winds. “You don’t want the truth” became “Sometimes, the truth can be hard to accept.” But I think my favorite edit was to the closing line: “Either way, I don’t give a damn what you think you’re entitled to” became “Either way, I respect your perspective.” Friendlier, yes. What the author was going for, no.
Describe Your Change verdict
This new addition to Writing Tools only swung and missed on one of the three tests I threw its way, and in that instance, Writing Tools warned me that it was not really equipped to do what I was asking. In the other instances, Describe Your Change definitely struck the tone that I was looking for, and did so in a way that gave me finer control than the original presets in Writing Tools offered.
I think there are still limitations. One test I thought about including but eventually abandoned involved the passive voice — something a lot of writers struggle with. But asking Describe Your Change to “remove the passive voice” or “use active verbs” didn’t produce tangible results, leading me to conclude that’s not something the feature is really designed to do.
I’m not totally sold on Writing Tools yet. Even with the largely successful changes in tone, the AI still left behind some awkward sentences and phrases that didn’t always sound natural. Anyone using Writing Tools to check tone should still closely review any changes to make sure your intent hasn’t been drastically altered or that confusing word choice hasn’t been introduced to the text. And frankly, double-checking Writing Tools’ handiwork might take longer than just handling the editing yourself.
Still, it’s encouraging to see a tool I didn’t have much use for evolve from one iOS update to the next. Even if I never fully embrace Writing Tools it’s a positive sign for the rest of Apple Intelligence that Apple realizes there’s work still to be done to make its AI tools even better.